You can get hepatitis B
- at birth, from a mother with hepatitis B to her baby.
- when blood from an infected person touches an open wound (sores, cuts) of another person.
- during vaginal or anal sex without a condom.
- through traditional or cultural practices that may involve blood e.g., tattoos, body piercing, acupuncture.
- through injections, medical and dental procedures in countries where the equipment is not sterilised (cleaned) properly. In Australia, these are safe.
- by sharing personal items that may have blood on them, like toothbrushes razors or intimate products.
- by sharing equipment used for injecting drugs.
You cannot get hepatitis B from
- coughing or sneezing.
- kissing, hugging or holding hands.
- mosquito or other insect bites.
- sharing food, eating utensils, or drinking glasses.
- sharing toilets.
- swimming pools.
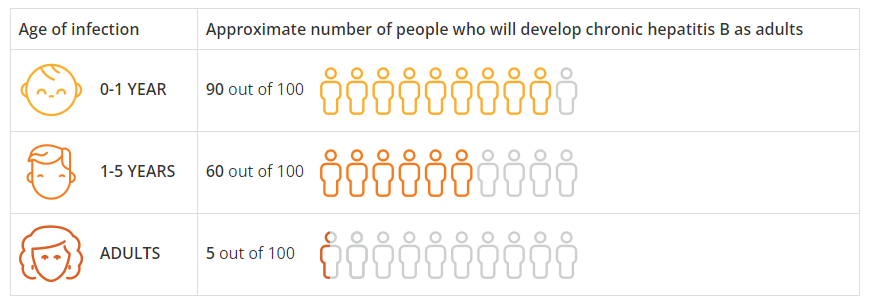
The younger a person is when they get hepatitis B, the higher the risk of developing chronic hepatitis B as an adult.